
“Sensory development issues are characterized by the ways that an individual processes sensory information. Generally, those with sensory developmental concerns are assumed to have difficulty handling loud noises or bright lights. However, there are many ways that sensory developmental disorders can present.” [1]
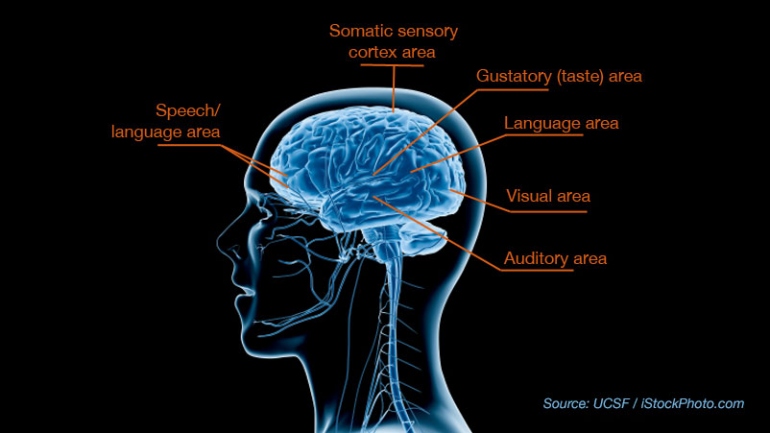
“Different types of sensory disabilities affect one or more senses; sight, hearing, smell, touch, taste or spatial awareness.
As 95% of the information about the world around us comes from our sight and hearing, a sensory disability can affect how a person gathers information from the world around them.” [2]
“The main causes of sensory disabilities include accidents or injury, genetic factors, illnesses, or environmental factors. Some of the sensory disabilities can be corrected through surgery, while others are long-life disorders.” [3]

4 Most Common Types of Sensory Disabilities
Sensory disabilities can be divided into the following types:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Blindness and Low Vision
- Sensory Processing Disorder
- Hearing Loss and Deafness

1. Autism Spectrum Disorder
“Autism spectrum disorder is a multiplex development condition that necessitates persevering challenges in non-verbal or verbal communication, social interaction, and repetitive behaviors. The symptoms of ASD vary from person to person. Being a lifelong developmental disability, Autism spectrum disorder affects the way an individual interacts with those around him.” They also have difficulties in communication and social interactions. Autism spectrum disorder may be caused due to genetics or environmental factors.” [4]
2. Blindness and Low Vision
“Blindness and low vision” covers a broad variety of definitions, including legal blindness, limited visual acuity, and color blindness. People with low vision have different experiences from people who are blind. Blind persons may use mobility aids, including canes and guide dogs.
Low vision usually interferes with the performance of daily activities, such as reading or driving. Persons with low vision may prefer to read large print. A person with low vision may not recognize images at a distance or be able to differentiate between colors of similar hues.
Causes: Uncorrected refractive errors, Cataract, Age-related macular degeneration, Glaucoma and/or Trachoma.” [5]

3. Sensory Processing Disorder
“SPD is formerly referred to as sensory integration dysfunction. It is a neurological condition that interferes with the body’s ability to interpret sensory messages from the brain and convert those messages into appropriate motor and behavioral responses. Sensory Processing Disorder makes patients have difficulties filtering out unimportant sensory information (like the background noise of a busy school hallway) and causing them to feel overwhelmed and over-stimulated in certain environments.
Common Symptoms:
- Be unable to tolerate bright lights and loud noises like ambulance sirens
- Refuse to wear clothing because it feels scratchy or
- Be distracted by background noises that others don’t seem to hear
- Be fearful of surprise touch, avoid hugs and cuddling even with familiar adults
- Be overly fearful of swings and playground equipment”
Often have trouble understanding where their body is in relation to other objects or people Treatment is usually done through therapy. Research shows that starting therapy early is key for treating SPD.“
4. Hearing loss and deafness
“Hearing loss, also known as a hearing impairment, is the partial or total inability to hear. If someone has very little or no hearing, the term ‘deaf’ may be used.
Damage to any part of the external, middle, or inner ear can cause hearing loss which can range from being mild to profound. Causes of hearing loss can be quite varied and can include problems with the bones within the ear, damage to the cochlear nerve, exposure to noise, genetic disorders, exposure to diseases in utero, age, trauma, and other diseases.” [2]
What causes sensory disabilities?
“Sensory disabilities have a wide range of causes depending on the specific type of sensory disability. They can be congenital, meaning someone is born with them due to a genetic mutation or maternal illness; or they can be genetic, meaning there is some alteration in genetic material that causes the impairment; or they can be metabolic, meaning a chronic illness or lifestyle-related cause affects someone’s senses; or they can be due to a physical injury which impairs a person’s senses. Whatever the specific cause of a person’s sensory disability, they all share a common factor: impaired neurological function.” [6]
What kind of support do people with sensory disabilities need?
Depending on an individual’s sensory disability and the specific needs that may arise to accommodate it, there are many resources available, including therapy, devices that can improve a person’s quality of life and the amazing Direct Support Professionals.
A Direct Support Professional (DSP) is someone who works directly with people who have intellectual or developmental disabilities. DSPs aim to assist people in realizing their full potential. They help people become integrated and engaged in their community.

Resources
[3] https://www.enableme.ke/en/article/4-most-common-types-of-sensory-disabilities-1535
[4] https://nuprisma.com/sensory-disabilities-types-effects-and-treatment/
[5] https://kines.rutgers.edu/dshw/disabilities/sensory/1061-sensory-disabilities [6] https://mapleservices.com.au/types-of-sensory-disabilities-and-impairment/
